Recent leaks claiming that the Vatican would be facing bankruptcy added to the statements made by the investigative author Gianluigi Nuzzi in his just-published book “Giudizio Universale”, have caused a stir in Rome despite the denials of two leading bishops.
In the book “Giudizio Universale” (Universal Judgement), Italian journalist Gianluigi Nuzzi exposed unpublished documents about the deteriorated Vatican’s financial situation. The author ensures that financial and real estate assets mismanagement, along with a notorious decrease in donations, are the main reason why the Vatican is facing bankruptcy.
Dramatic loss
According to the book published last October 21, last year, the Holy See lost 44 million euros. Nuzzi claims that at the edge of bankruptcy, the measures the Pope has been taking are not enough. The situation is so severe that last year, the Church decided to sell families’ jewellery such as the property “Santa María de Galería,” 424 hectares on the outskirts of Rome.
Decline of donations
The data presented in the book shows that the contributions to the Church, known as “Obolo de San Pedro,” have been reduced by half in a decade (from 101 million in 2006 to 51 in 2008). Because of the crisis, 58% of the received amount serves to clean up accounts, and only 20% remain as a deposit. As Nuzzi explained, the result is that of each ten euros, only two end up serving the purpose of helping those in need.
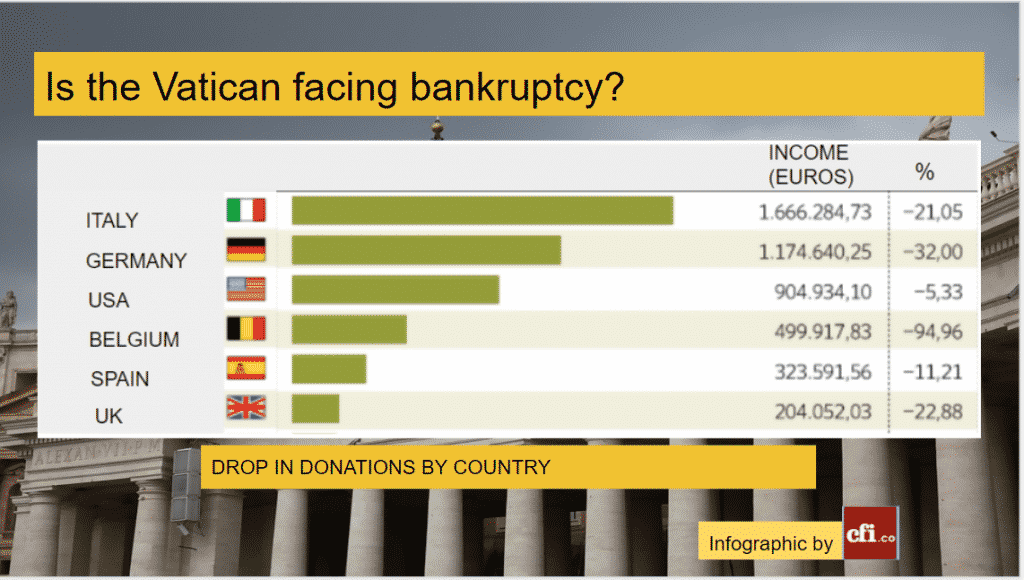
A surprising fact the journalist and author describes is the origin of the donations: dioceses are the first source, foundations come in second place, and private donors come just in third place. Italy and Germany are the most prominent supporters with more than 1.5 million euros each; their support decreased by more than 20%.
The official response
The head of the Administration of the Patrimony of the Apostolic See (APSA), Bishop Nunzio Galantino, promptly denied that the finances of the Holy See were about to go bankrupt. “There’s no bankruptcy or default here. There’s only a need for a spending review,” Galantino insisted. “The ordinary management of the APSA in 2018 closed with a profit of over 22 million,” he expressed to the “Vatican News.”
Regarding the properties managed by the APSA and the accusations of mismanagement, Galantino explained that they include 2,400 apartments located mostly in Rome and Castel Gandolfo plus another 600 shops and offices.
In response to Nuzzi’s statement that 40% of the patrimony doesn’t grant income, Galantino explained that those not generating revenue are service apartments or offices of the Curia. He also told that about 60% of the apartments are rented for reduced rent, to employees in need.
He considered this a kind of social housing, something that, when done by private companies, is praised, but when it’s the Vatican doing it, it is considered incompetent.
“There is no threat of collapse or default here. There is only the need for a spending review. And that is what we’re doing. I can prove it to you with numbers,” Galantino said on October 22.
Is the Vatican facing bankruptcy or not?
This is something that only time will reveal. So far, the bells of broke seem to be tolling despite the official statements.
See also about Business Risks.